VXLAN Flood and learn configuration on Nexus 9000
Virtual eXtensible Local Area Network (VXLAN) is an overlay technology described in RFC 7348. It allows layer-2 frames to be tunneled through an IP network.
The goal is to carry layer 2 traffic on top of a more extensible media. Layer 2 is historically convenient for many types of applications. While new ones should avoid relying on it, the use case is often encountered.
It has been created for massively scalable datacenter
– to overcome current layer-2 protocols scalability issues
– to allows more flexible layer-2 networks
– to accommodate with multi-tenancy
There are multiple implementations for VXLAN with or without control plane.
The following article deals with simple flood and learn implementation on Nexus 9K platform with IGP and multicast in the underlay.
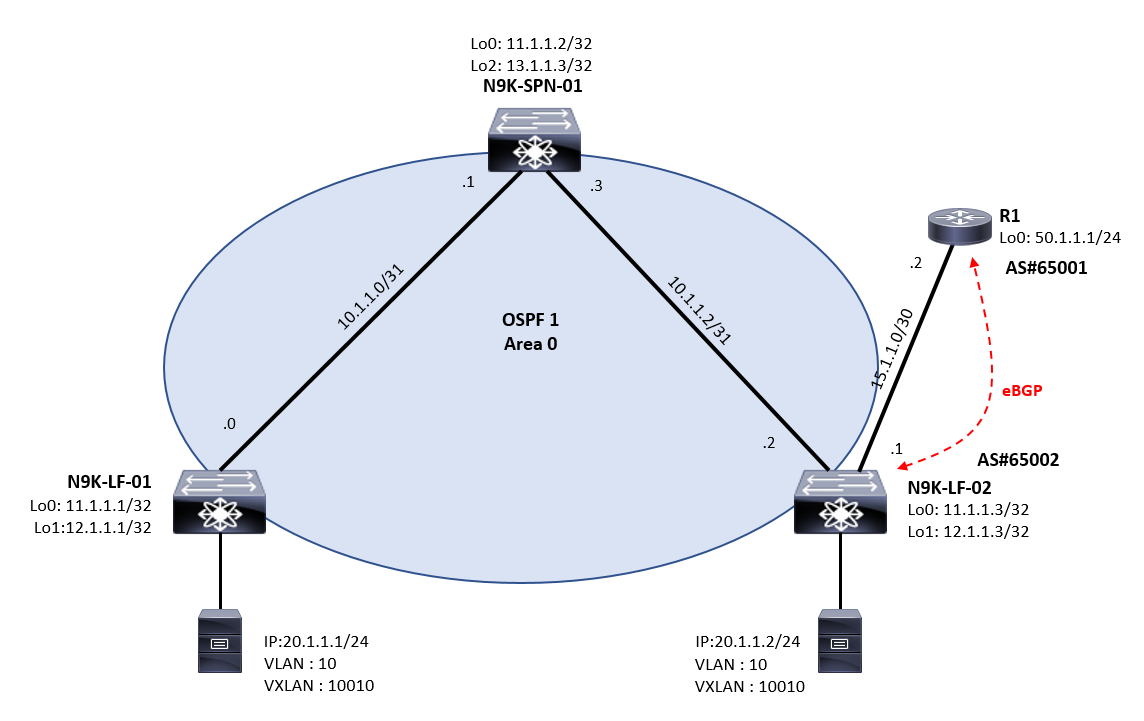
First of all, we need to build the underlay, it is a standard routed IP network with multicast enabled on top of it.
– IGP: OSPF
– Multicast routing: PIM
N9K-LF-01
feature ospf
feature pim
!
interface Ethernet1/1
description TO_SPINE
no switchport
mtu 9216
ip address 10.1.1.0/31
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
!
ip pim rp-address 13.1.1.3 group-list 239.0.0.0/8
!
interface loopback0
description RID
ip address 11.1.1.1/32
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
!
interface loopback1
description VTEP
ip address 12.1.1.1/32
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
!
router ospf 1
router-id 11.1.1.1
auto-cost reference-bandwidth 100000 Mbps
Do not forget to create two loopbacks:
– one for the router id in the underlay,
– one for the VTEP IP
The OSPF reference bandwidth may be changed as well as we are heading to the 100G.
N9K-LF-02
feature ospf
feature pim
!
interface Ethernet1/1
description TO_SPINE
no switchport
mtu 9216
ip address 10.1.1.2/31
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
!
ip pim rp-address 13.1.1.3 group-list 239.0.0.0/8
!
interface loopback0
description RID
ip address 11.1.1.3/32
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
!
interface loopback1
description VTEP
ip address 12.1.1.3/32
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
!
router ospf 1
router-id 11.1.1.3
auto-cost reference-bandwidth 100000 Mbps
In our case a static RP will be declared on the spine.
N9K-SPN-01
feature ospf
feature pim
!
ip pim rp-address 13.1.1.3 group-list 239.0.0.0/8
!
interface Ethernet1/1
no switchport
mtu 9216
ip address 10.1.1.1/31
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
!
interface Ethernet1/2
no switchport
mtu 9216
ip address 10.1.1.3/31
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
!
interface loopback0
ip address 11.1.1.2/32
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
!
interface loopback2
description MCAST-RP
ip address 13.1.1.3/32
ip router ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
!
router ospf 1
router-id 11.1.1.2
auto-cost reference-bandwidth 100000 Mbps
Ensure that OSPF neighorship is OK and that VTEP loopback reachability is proper.
Once done, activate the VTEP interface (nve) and associate the VNI to the VLAN.
N9K-LF-01
feature vn-segment-vlan-based
feature nv overlay
!
vlan 10
name SRV-1
vn-segment 10010
!
interface nve1
no shutdown
source-interface loopback1
member vni 10010
mcast-group 239.1.1.1
!
interface Ethernet1/2
description TO_HOST
switchport access vlan 10
N9K-LF-02
feature vn-segment-vlan-based
feature nv overlay
!
vlan 10
name SRV-1
vn-segment 10010
!
interface nve1
no shutdown
source-interface loopback1
member vni 10010
mcast-group 239.1.1.1
!
interface Vlan10
no shutdown
ip address 20.1.1.254/24
!
interface Ethernet1/2
description TO_HOST
switchport access vlan 10
You can validate proper operation and MAC learning with usual commands. The MAC address table should point some entries towards the remote VTEP.
ping
show mac address table
Other show commands are available to validate VXLAN / VTEP configuration.
See below a capture of the frame encapsulated inside a VXLAN header. The ping is performed from one host towards an external destination (represented by R1 loopback).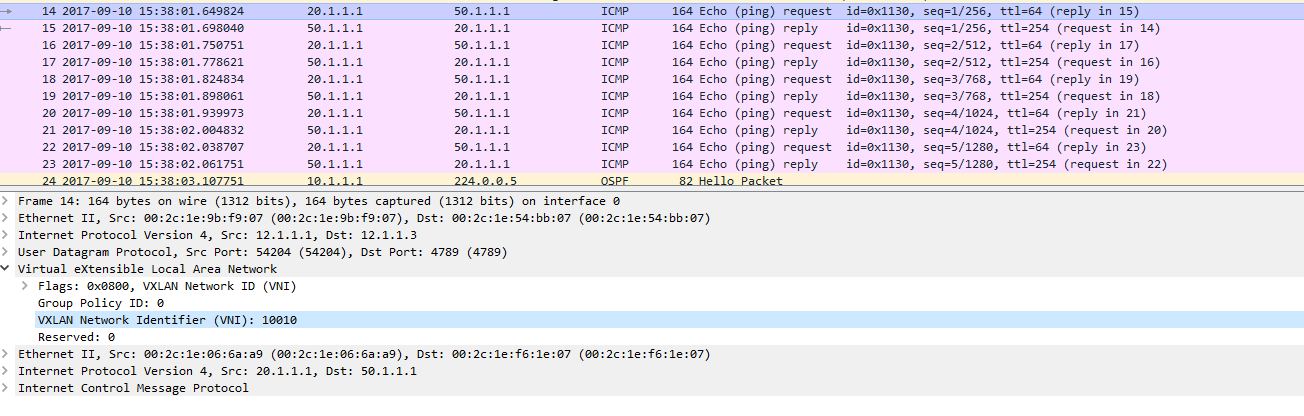
HTH.