IOS XR Basic IS-IS and iBGP configuration
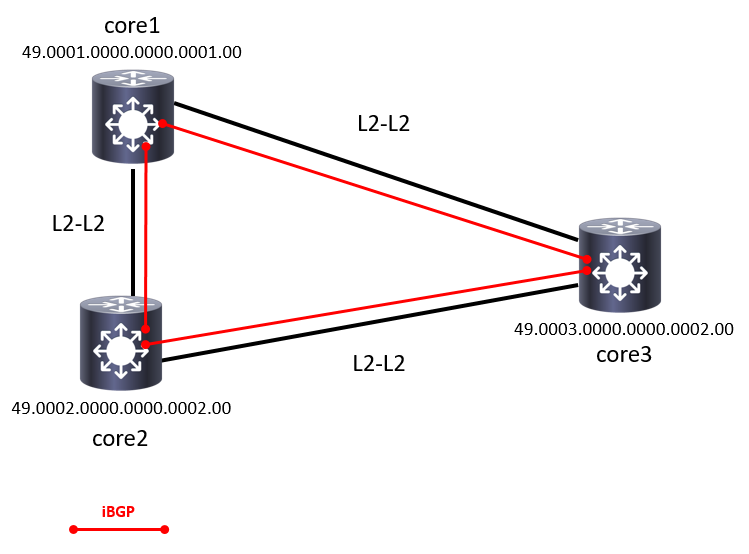
In this topology we are building a small core network made of 3 routers.
Those 3 routers will run basic IS-IS (intermediate-system to intermediate-system) routing protocol as IGP. Once the IGP is OK a full mesh iBGP will be configured.
For IS-IS we will proceed with integrated IS-IS as we are carrying IP prefixes.
Each of the routers are located in a different site in this scenario so I decided to configure each one of them in separate area. Thus all the peering between the core routers will be L2 type only.
The area is determined by the NET (Network Entities Title) adress which is in CLNS format (ISO adressing scheme)
core1 – 49.0001.0000.0000.0001.00
core2 – 49.0002.0000.0000.0002.00
core3 – 49.0003.0000.0000.0003.00
Decrypted NSAP:
– Area : 49.0001 (49 is the private AFI ID number, 0001 the area)
– System ID: 0000.0000.0001 (router-id)
– NSEL: 00 (identify upper layer processing, 00 indicates that it is NET adressing, that it is the router itself)
Once done let’s check ipv4 config in the core:
RP/0/0/CPU0:core1#sho ip int brief
Tue Jun 20 21:27:28.830 UTC
Interface IP-Address Status Protocol
MgmtEth0/0/CPU0/0 unassigned Shutdown Down
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 13.13.3.1 Up Up
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1 13.13.2.1 Up Up
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2 13.13.0.1 Up Up
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/3 unassigned Shutdown Down
RP/0/0/CPU0:core2#sho ip int brief
Tue Jun 20 21:27:56.599 UTC
Interface IP-Address Status Protocol
MgmtEth0/0/CPU0/0 unassigned Shutdown Down
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 13.13.4.2 Up Up
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1 13.13.2.2 Up Up
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2 13.13.1.2 Up Up
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/3 unassigned Shutdown Down
RP/0/0/CPU0:core3#sho ip int brief
Tue Jun 20 21:28:23.307 UTC
Interface IP-Address Status Protocol
MgmtEth0/0/CPU0/0 unassigned Shutdown Down
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 13.13.5.3 Up Up
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1 unassigned Shutdown Down
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2 13.13.0.3 Up Up
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/3 13.13.1.3 Up Up
OK let’s proceed to the IS-IS configuration. Remember that IOS-XR is very hierarchical.
Put each NET address on the routers and configure the interface that interconnect them as IS-IS level-2 capable circuit.
I split my three routers in different areas as they would be in different geographical locations. The connection of all of them results in a backbone network, so all the neighbor relationship are L2.
Once done, place them in the IPv4 AF and commit!
router isis core1
net 49.0001.0000.0000.0001.00
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1
circuit-type level-2-only
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2
circuit-type level-2-only
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
!
!
router isis core2
net 49.0002.0000.0000.0002.00
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1
circuit-type level-2-only
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2
circuit-type level-2-only
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
!
!
router isis core3
net 49.0003.0000.0000.0003.00
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2
circuit-type level-2-only
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/3
circuit-type level-2-only
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
!
!
Neighbors can easily be checked using the following commands
– show isis interface
– show isis neighbors
RP/0/0/CPU0:core1#sho isis neighbors
Tue Jun 20 21:32:48.549 UTC
IS-IS core1 neighbors:
System Id Interface SNPA State Holdtime Type IETF-NSF
core2 Gi0/0/0/1 0043.f70d.7a02 Up 28 L2 Capable
core3 Gi0/0/0/2 0043.f740.4003 Up 21 L2 Capable
RP/0/0/CPU0:core1#sho ip route 13.13.1.0/24
Tue Jun 20 21:33:36.365 UTC
Routing entry for 13.13.1.0/24
Known via "isis core1", distance 115, metric 20, type level-2
Installed Jun 20 21:15:23.270 for 00:18:13
Routing Descriptor Blocks
13.13.2.2, from 13.13.2.2, via GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1
Route metric is 20
13.13.0.3, from 13.13.0.3, via GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2
Route metric is 20
No advertising protos.
Let’s configure loopback and announce them with IS-IS :
– core 1: 1.1.1.1/32
– core 2: 1.1.1.2/32
– core 3: 1.1.1.3/32
RP/0/0/CPU0:core1#conf t
RP/0/0/CPU0:core1(config)#int loopback 0
RP/0/0/CPU0:core1(config-if)#ipv4 address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
RP/0/0/CPU0:core1(config-if)#router isis core1
RP/0/0/CPU0:core1(config-isis)#interface lo 0
RP/0/0/CPU0:core1(config-isis-if)#passive
RP/0/0/CPU0:core1(config-isis-if)#address-family ipv4 unicast
RP/0/0/CPU0:core1(config-isis-if-af)#commit
Routes are correctly learned
RP/0/0/CPU0:core1#sho ip route is
Tue Jun 20 21:44:08.242 UTC
i L2 1.1.1.2/32 [115/10] via 13.13.2.2, 00:01:03, GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1
i L2 1.1.1.3/32 [115/10] via 13.13.0.3, 00:00:15, GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2
i L2 13.13.1.0/24 [115/20] via 13.13.0.3, 00:00:15, GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2
[115/20] via 13.13.2.2, 00:00:15, GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1
Reachability is OK between the loopbacks it is then possible to setup our full-mesh iBGP.
RP/0/0/CPU0:core1#ping 1.1.1.2 source 1.1.1.1
Tue Jun 20 21:44:27.941 UTC
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 1.1.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/8/29 ms
RP/0/0/CPU0:core1#ping 1.1.1.3 source 1.1.1.1
Tue Jun 20 21:44:32.840 UTC
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 1.1.1.3, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/11/39 ms
Initialize the routing protocol
router bgp 65001
bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
address-family ipv4 unicast
Create a neighbour group that will centralize the configurations related to the internal peers.
This will reduce the overall configuration size.
neighbor-group CORE
remote-as 65001
update-source Loopback0
address-family ipv4 unicast
Then affect the peers to the neighbor group
neighbor 1.1.1.2
use neighbor-group CORE
!
neighbor 1.1.1.3
use neighbor-group CORE
The action is performed on all routers and peerings are brought up:
RP/0/0/CPU0:core1#sho bgp summary
Tue Jun 20 22:12:51.564 UTC
BGP router identifier 1.1.1.1, local AS number 65001
BGP generic scan interval 60 secs
BGP table state: Active
Table ID: 0xe0000000 RD version: 0
BGP main routing table version 1
BGP scan interval 60 secs
BGP is operating in STANDALONE mode.
Process RcvTblVer bRIB/RIB LabelVer ImportVer SendTblVer StandbyVer
Speaker 1 1 1 1 1 1
Neighbor Spk AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down St/PfxRcd
1.1.1.2 0 65001 3 4 1 0 0 00:01:26 0
1.1.1.3 0 65001 2 3 1 0 0 00:00:53 0
HTH.
Links:
IOS XR routing reference guide: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios_xr_sw/iosxr_r3-2/routing/configuration/guide/rt_c32.pdf