Simple Cisco Zone Based Firewall Lab
Zone Based Firewall (or ZBF, ZBFW or ZFW) is the actual firewall feature available on Cisco routers. ZBF is destined to replace (or remodeled) the IOS classic stateful firewall also called CBAC (Context Based Access Control).
ZBF provides stateful packet inspection (compared to ACL, stateless) and offers a flexible CLI configuration that I will detail below.
ZBF is a great feature for small and midsized networks needing security isolation between multiple zones having different purposes and access rights. The configuration is easier compared to CBAC that requires inspection rules for each interfaces.
Keep this rules in mind while configuring ZBF:
– Zone to zone communication is implicitly denied
– Interfaces in the same zone are allowed to talk to each other
– The self zone is the router: it designates all traffic originated and destined to the router. This is allowed by default.
The basic scenario consists in defining 3 zones: Private, DMZ and Internet:
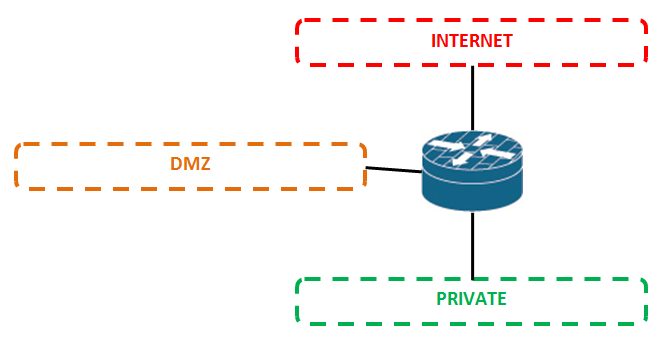
But the following scenarios can also be considered:
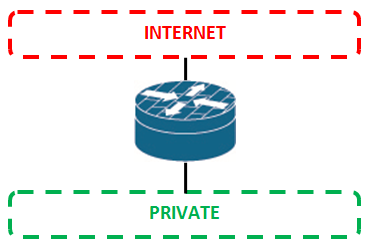
– 2 zones: LAN and EXTERNAL as simple firewall
– Multiple service zones: enforce a corporate network security policy
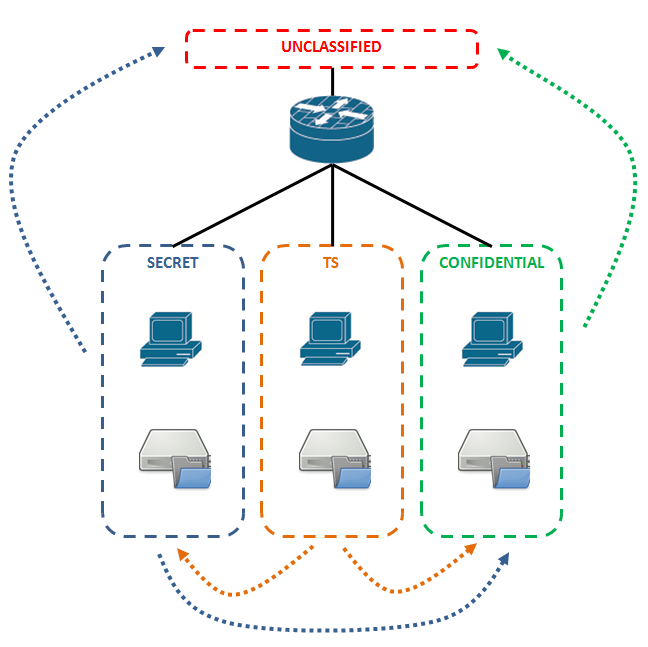
I will explore the configuration of the last scenario. Imagine a company that classifies data according to different levels. To maintain the isolation the company designs its network using multiple servers residing in different networks. A Cisco router is used to inspect and log file transfer traffic between these networks. The administrators of the router are located in the CONFIDENTIAL zone.
The following steps are required to set up ZBFW:
– Create zones
– Put the interfaces in zones
– Define ACLs and Class-Maps to select the traffic
– Define policies applied (drop, inspect, pass, log)
– Define where filtering occurs (zone-pair)
In this example:
Create the security zones
zone security PUBLIC
description PUBLIC-UNCLASSIFIED
zone security TS
description TOP-SECRET
zone security SECRET
description SECRET
zone security CONFIDENTIAL
description CONFIDENTIAL
R13#show zone security
zone self
Description: System defined zone
zone PUBLIC
Description: PUBLIC-UNCLASSIFIED
zone TS
Description: TOP-SECRET
zone SECRET
Description: SECRET
zone CONFIDENTIAL
Description: CONFIDENTIAL
Define the interfaces, here I configure a router on a stick with 802.1q sub interfaces.
int f0/0
no sh
int f0/0.10
encapsulation dot1Q 10
ip address 10.10.10.254 255.255.255.0
zone-member security SECRET
int f0/0.20
encapsulation dot1Q 20
ip address 10.10.20.254 255.255.255.0
zone-member security CONFIDENTIAL
int f0/0.30
encapsulation dot1Q 30
ip address 10.10.30.254 255.255.255.0
zone-member security TS
int lo0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
zone-member security PUBLIC
The interfaces now appear under their zones:
R13#sh zone security
zone self
Description: System defined zone
zone PUBLIC
Description: PUBLIC-UNCLASSIFIED
Member Interfaces:
Loopback0
zone TS
Description: TOP-SECRET
Member Interfaces:
FastEthernet0/0.30
zone SECRET
Description: SECRET
Member Interfaces:
FastEthernet0/0.10
zone CONFIDENTIAL
Description: CONFIDENTIAL
Member Interfaces:
FastEthernet0/0.20
R13#sh ip int brie
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 unassigned YES unset up up
FastEthernet0/0.10 10.10.10.254 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/0.20 10.10.20.254 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/0.30 10.10.30.254 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Loopback0 1.1.1.1 YES manual up up
Then I configure the policies that will enforce zone to zone communication restrictions.
Like QoS configuration, class-maps and ACLs match the traffic and policy-maps take the actions.
ip access-list standard DENIED
deny any
class-map type inspect match-any filetransfer
match protocol nfs
class-map type inspect match-all LOGDENIED
match access-group name DENIED
policy-map type inspect pol-filetransfer
class type inspect filetransfer
inspect
class class-default
drop log
policy-map type inspect pol-LOGDENIED
class type inspect LOGDENIED
drop log
Then I apply the policies between the zones:
zone-pair security CONFIDENTIAL->UNCLASSIFIED source CONFIDENTIAL destination PUBLIC
service-policy type inspect pol-filetransfer
zone-pair security SECRET->CONFIDENTIAL source SECRET destination CONFIDENTIAL
service-policy type inspect pol-filetransfer
zone-pair security SECRET->UNCLASSIFIED source SECRET destination PUBLIC
service-policy type inspect pol-filetransfer
zone-pair security TS->UNCLASSIFIED source TS destination PUBLIC
service-policy type inspect pol-filetransfer
zone-pair security TS->CONFIDENTIAL source TS destination CONFIDENTIAL
service-policy type inspect pol-filetransfer
zone-pair security TS->SECRET source TS destination SECRET
service-policy type inspect pol-filetransfer
zone-pair security PUBLIC->TS source PUBLIC destination TS
service-policy type inspect pol-LOGDENIED
zone-pair security PUBLIC->CONFIDENTIAL source PUBLIC destination CONFIDENTIAL
service-policy type inspect pol-LOGDENIED
zone-pair security PUBLIC->SECRET source PUBLIC destination SECRET
service-policy type inspect pol-LOGDENIED
Last but not least, I configure the self zone to only permit administrators to access the router. By default any zone can communicate with any router interfaces.
!from ZONE SECRET to routers loopback 2 (not member of any zone)
R2(config)#do ping 2.2.2.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 2.2.2.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 20/22/32 ms
(as you see I avoid using match protocol with the self zone, because it is buggy… CSCsq44101)
ip access-list extended ADMIN-ACL
permit tcp any any eq 22
permit tcp any any eq telnet
permit tcp any any eq cmd
permit tcp any any eq tacacs
permit tcp any any eq 37
permit icmp any any
class-map type inspect match-any ADMIN
match access-group name ADMIN-ACL
policy-map type inspect pol-ADMIN
class type inspect ADMIN
inspect
class class-default
drop log
zone-pair security CONFIDENTIAL->self source CONFIDENTIAL destination self
service-policy type inspect pol-ADMIN
zone-pair security self->CONFIDENTIAL source self destination CONFIDENTIAL
service-policy type inspect pol-LOGDENIED
zone-pair security self->SECRET source self destination SECRET
service-policy type inspect pol-LOGDENIED
zone-pair security self->TS source self destination TS
service-policy type inspect pol-LOGDENIED
Let’s test again:
R2(config)#do ping 2.2.2.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 2.2.2.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
.....
It works!
The following commands can be useful to troubleshoot Zone Based Firewall:
sh class-map type inspect
sh policy-map type inspect
sh ip access-list
sh zone security
sh zone-pair security
Please note that ZBF can be configured with SDM.
Thanks for reading!
Links:
http://blogs.cisco.com/cin/zone_based_firewalls/
http://tools.cisco.com/security/center/content/CiscoSecurityAdvisory/cisco-sa-20120328-zbfw
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/secursw/ps1018/products_tech_note09186a00808bc994.shtml
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk828/technologies_tech_note09186a00800f67d5.shtml