IPv6 transition and MPLS 6VPE lab
Today we are going to work on an IPv6 transition mechanism called 6VPE.
6VPE/6PE uses the underlying IPv4 MPLS/MPLS VPN network to carry IPv6 packets.
To realize this lab, PE routers and route-reflectors need to be IPv6/VPNv6 ready. P routers forward packets based on MPLS information ignoring the layer 3.
Based on LACNIC drawings, here’s a brief explanation
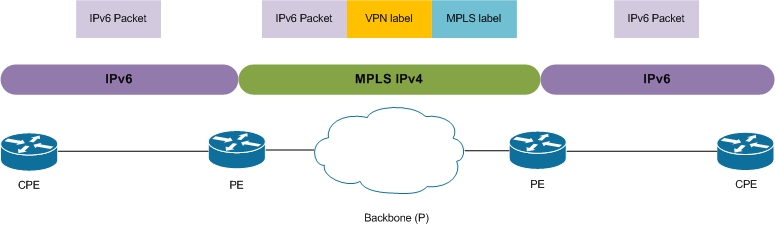
The topology:
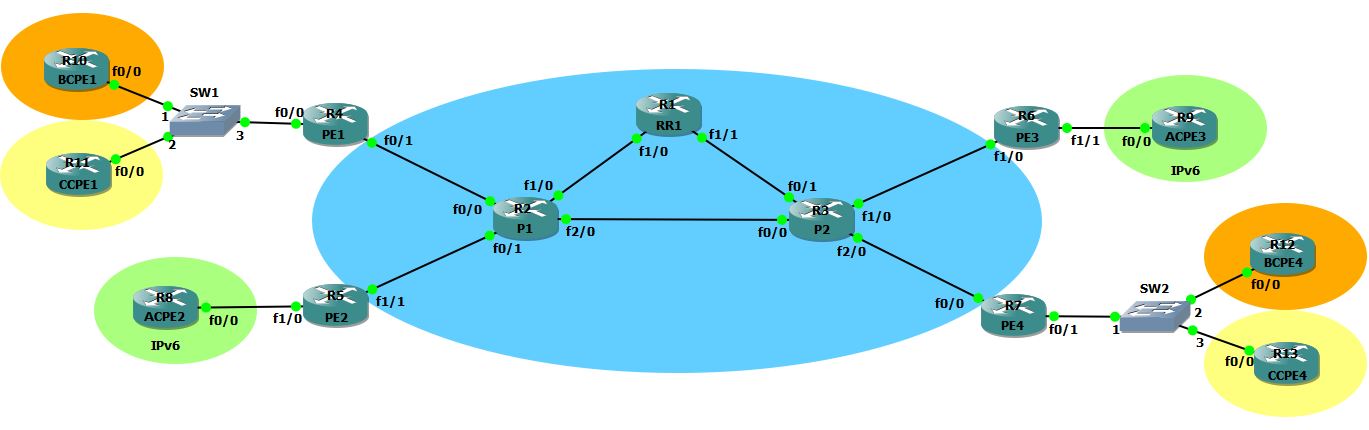
Pros:
– Only RR, PE and CPE need IPv6
– P core routers are left unchanged
– No need to run a dual stack network (IP/IPv6, OSPF/OSPFv3)
– Possible to have dual stack customers
– Non disruptive
Prerequisites:
– A MPLS VPN network
– RR, PE, and CPE IPv6 ready (hardware processing must be supported)
Steps:
– IPv6/VPNv6 compatible MP-BGP between RR1 and all the PEs,
– VRFs v6 for each customers on the PEs,
– IPv6 compatible (and supported…) routing protocol for PE-CE communication. It is also possible to set static routes (redistribute static and connected).
Route reflector configuration (activate IPv6 routing, VPNv6 peering)
ipv6 unicast-routing
!
router bgp 65000
address-family vpnv6
neighbor RRCLIENT send-community both
neighbor RRCLIENT route-reflector-client
neighbor 5.5.5.5 activate
neighbor 6.6.6.6 activate
exit-address-family
PE configuration
ip vrf becomes vrf definition, ip vrf forwarding becomes vrf forwarding
The statement address-family ipv4 in the VRF definition is needed to use the command ping vrf X…
ipv6 unicast-routing
ipv6 cef
!
vrf definition A
description Customer A
rd 65000:3
!
address-family ipv4
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6
route-target export 65000:3
route-target import 65000:3
exit-address-family
!
interface FastEthernet1/0
vrf forwarding A
no ip address
duplex full
speed 100
ipv6 address 2001::1/64
ipv6 address autoconfig
!
router bgp 65000
address-family vpnv6
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community both
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6 vrf A
redistribute static
redistribute connected
no synchronization
exit-address-family
!
ipv6 route vrf A 2008::/64 2001::2
CPE configuration
ipv6 unicast-routing
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
no ip address
speed 100
full-duplex
ipv6 address 2001::2/64
ipv6 address autoconfig
!
ipv6 route ::/0 2001::1
Let’s have a closer look to the path
First the packet is sent out ACPE2 thanks to default route.
ACPE2#sh ipv route static
IPv6 Routing Table - 7 entries
S ::/0 [1/0]
via 2001::1
It enters PE2 in VRF A. The VRF A routing table shows us a recursive lookup inside the default IPv4 routing table.
PE2#sh ipv route vrf A
...
B 2002::/64 [200/0]
via 6.6.6.6%default, indirectly connected
B 2009::/64 [200/0]
via 6.6.6.6%default, indirectly connected
...
PE2#sh ip route 6.0.0.0
Routing entry for 6.0.0.0/32, 1 known subnets
O 6.6.6.6 [110/4] via 52.52.52.2, 00:12:43, FastEthernet1/1
To reach the 6.6.6.6 the packet will use MPLS switching (label 28)
PE2#sh mpls forwarding-table 6.6.6.6
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes Label Outgoing Next Hop
Label Label or Tunnel Id Switched interface
22 28 6.6.6.6/32 0 Fa1/1 52.52.52.2
The MPLS VPN tag is 35
PE2#sh ip bgp vpnv6 unicast all labels
Network Next Hop In label/Out label
Route Distinguisher: 65000:3 (A)
2001::/64 :: 34/nolabel
2002::/64 ::FFFF:6.6.6.6 nolabel/34
2008::/64 2001::2 36/nolabel
2009::/64 ::FFFF:6.6.6.6 nolabel/35
To sum it up, the CEF entry
PE2#sh ipv cef vrf A
2009::/64
nexthop 52.52.52.2 FastEthernet1/1 label 28 35
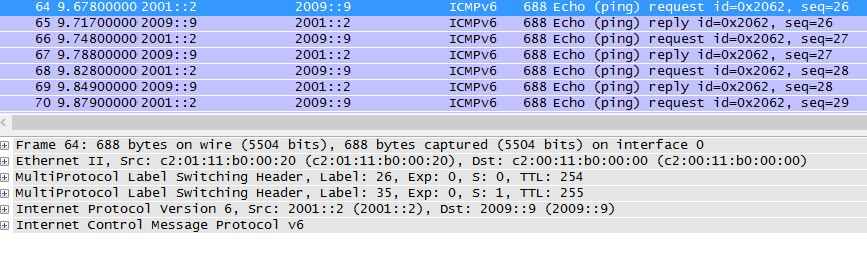
On P1 the packet is switched
P1#sh mpls forwarding-table 6.6.6.6
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop
tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface
28 26 6.6.6.6/32 164380 Fa2/0 23.23.23.3
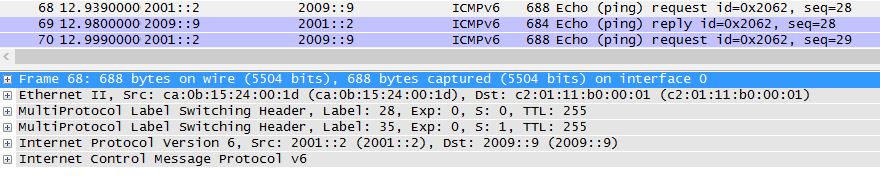
On P2 the tag is removed due to PHP. Only one tag remains, the VPN tag.
P2#sh mpls forwarding-table 6.6.6.6
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop
tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface
26 Pop tag 6.6.6.6/32 201008 Fa1/0 36.36.36.6
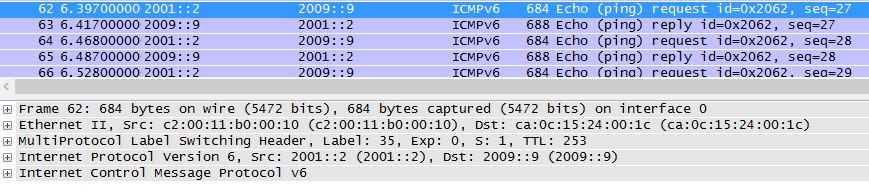
On PE3 the packet is transfered according the VPN tag:
PE3#sh mpls forwarding-table labels 35
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes Label Outgoing Next Hop
Label Label or Tunnel Id Switched interface
35 No Label 2009::/64[V] 182312 Fa1/1 2002::2
Troubleshooting commands
ping 2009::9 repeat 30
traceroute 2009::9
sh ipv6 int brief
sh ipv6 route vrf A
sh ipv6 cef vrf A
sh mpls forwarding-table
sh mpls forwarding-table vrf A
sh mpls forwarding-table labels 35
sh ip bgp vpnv6 unicast all
sh ip bgp vpnv6 unicast vrf A
sh ip bgp vpnv6 unicast all labels
Special thanks to Romain that made me discover this technology.
Links
http://lacnic.net/documentos/seminarios/6PE_6VPE_LACNIC.pdf
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/iosswrel/ps6537/ps6553/prod_presentation0900aecd80311df4.pdf
http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc4659.txt
http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4798
http://www.ipflow.utc.fr/index.php/6VPE_-_IPv6_VPN_over_MPLS