Wildcard masks, once and for all !
Network masks…
… indicate which part of an IP address is the network, and which part is the host
… are essential in routing decisions
Wildcard masks
… indicate which part of an IP address is variable
… are useful to express a matching condition
… can simplify configuration files
… are used because it is not possible to use network mask expressions
… make matching operations more efficient (processing)
In IOS configuration we can find them in:
– routing protocol network statements (OSPF)
– access control lists (ACLs)
Configurations example
ACLs
!
ip access-list extended RDP
deny tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 10.10.10.1 0.0.0.0 3389
permit ip any any
!
OSPF
!
router ospf 1
router-id 1.1.1.1
network 1.1.1.0 0.0.0.3
network 1.1.1.4 0.0.0.3
!
!
interface f1/0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
!
interface f1/1
ip address 1.1.1.5 255.255.255.252
!
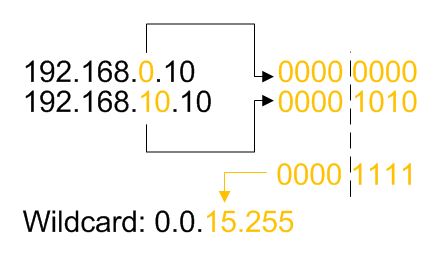
Reduction example:
Deny tcp 80 for these subnets 192.168.0.0/24 -> 192.168.10.0/24
!
ip access-list extended WWW
deny tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.15.255 any eq 80
permit ip any any
!
Deny udp 53 to these hosts 192.168.50.1/24 and 192.168.50.2/24
!
ip access-list extended DNS
deny udp any 192.168.50.1 0.0.0.3 eq 53
permit ip any any
!
To sum it up:
0 -> care
1 -> don’t care, can change