Cisco MPLS L3VPN lab
The topology used for Cisco MPLS lab has been slightly modified to work on MPLS L3VPNs, one of the possible use of MPLS technology.
MPLS L3VPNs provide isolation for customers of the same network. This is made possible thanks to VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding which are virtual and isolated routing and forwarding tables.
Prerequisites:
– A working MPLS network
We will implement the following technologies:
– MP-BGP between RR1 and all the PEs,
– VRFs for each customers on the PEs,
– a routing protocol for PE-CE communication.
Route reflector configuration
To switch to new BGP address-family configuration style, use the bgp upgrade-cli command
Route reflector: a route reflector is an iBGP functionality that permits to avoid iBGP full mesh by reflecting routes from one peer to another.
Peer group: a peer group enables two things: group all prefix updates in one BGP UPDATE message and reduce the BGP configuration.
VPNV4: a specific types of prefixes that combines a route distinguisher identifying the VRF and an IPv4 prefix.
router bgp 65000
bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor RRCLIENT peer-group
neighbor RRCLIENT remote-as 65000
neighbor RRCLIENT update-source Loopback0
neighbor 4.4.4.4 peer-group RRCLIENT
neighbor 5.5.5.5 peer-group RRCLIENT
neighbor 6.6.6.6 peer-group RRCLIENT
neighbor 7.7.7.7 peer-group RRCLIENT
!
address-family ipv4
no synchronization
neighbor RRCLIENT route-reflector-client
neighbor RRCLIENT soft-reconfiguration inbound
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 5.5.5.5 activate
neighbor 6.6.6.6 activate
neighbor 7.7.7.7 activate
no auto-summary
exit-address-family
!
address-family vpnv4
neighbor RRCLIENT send-community both
neighbor RRCLIENT route-reflector-client
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 5.5.5.5 activate
neighbor 6.6.6.6 activate
neighbor 7.7.7.7 activate
exit-address-family
PE1 configuration example
VRFs definition:
route distinguisher (rd): identifier corresponding to a VRFs
route-target (rt): indicates how routes are exchanged (transmitted as extended communities)
ip vrf B
description VRF Customer B
rd 65000:1
route-target export 65000:1
route-target import 65000:1
!
ip vrf C
description VRF Customer C
rd 65000:2
route-target export 65000:2
route-target import 65000:2
VRFs on interfaces
interface FastEthernet0/0.10
encapsulation dot1Q 10
ip vrf forwarding B
ip address 104.104.104.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/0.11
encapsulation dot1Q 11
ip vrf forwarding C
ip address 114.114.114.4 255.255.255.0
PE1-BCPE1 configuration
On P1:
router eigrp 65000
auto-summary
!
address-family ipv4 vrf C
redistribute bgp 65000 metric 1 1 1 1 1
network 0.0.0.0
auto-summary
autonomous-system 11
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf B
redistribute bgp 65000 metric 1 1 1 1 1
network 0.0.0.0
no auto-summary
autonomous-system 10
exit-address-family
!
router bgp 65000
bgp router-id 4.4.4.4
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 65000
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0
!
address-family ipv4 vrf C
redistribute eigrp 11
no synchronization
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf B
redistribute eigrp 10
no synchronization
exit-address-family
On ACPE1, traditional EIGRP:
router eigrp 10
network 0.0.0.0
no auto-summary
Verification on BCPE1
BCPE1#sh ip route
101.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 101.101.101.101 is directly connected, Loopback0
124.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D EX 124.124.124.0
[170/2560025856] via 104.104.104.4, 00:01:11, FastEthernet0/0
122.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D EX 122.122.122.122
[170/2560025856] via 104.104.104.4, 00:01:11, FastEthernet0/0
104.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 104.104.104.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
BCPE1#ping 122.122.122.122
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 122.122.122.122, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 84/84/88 ms
We can check on CCPE1 that customers B’s routes are not reachable
CCPE1#sh ip route
114.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 114.114.114.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
111.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 111.111.111.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
131.131.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D EX 131.131.131.0
[170/2560002816] via 114.114.114.4, 00:02:35, FastEthernet0/0
134.134.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D EX 134.134.134.0
[170/2560002816] via 114.114.114.4, 00:02:35, FastEthernet0/0
Examine the packet (BCPE1 to BCPE4)
As usual, the packet is switched and left unmodified until it reaches the PE router.
The packet enter the PE router:
PE1#sh ip route vrf B
Routing Table: B
...
101.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 101.101.101.101
[90/156160] via 104.104.104.10, 01:47:46, FastEthernet0/0.10
124.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 124.124.124.0 [200/0] via 7.7.7.7, 00:09:26
122.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 122.122.122.122 [200/156160] via 7.7.7.7, 00:09:26
104.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 104.104.104.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0.10
The MPLS VPN tag (39):
PE1#show ip bgp vpnv4 all labels | i 7.7.7.7
7.7.7.7 nolabel/39
124.124.124.0/24 7.7.7.7 nolabel/38
131.131.131.0/24 7.7.7.7 nolabel/40
134.134.134.0/24 7.7.7.7 nolabel/41
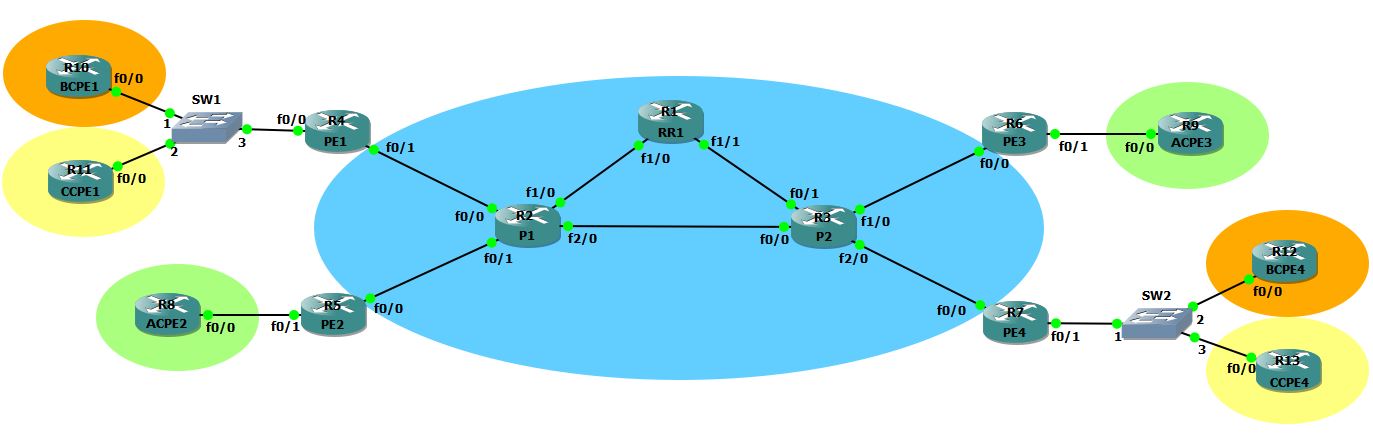
The next-hop is 7.7.7.7, however 7.7.7.7 is not reachable from the PE RT, but is present in the MPLS LFIB (27)
PE1#sh mpls forwarding-table | i 7.7.7.7
Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop
30 27 7.7.7.7/32 0 Fa0/1 42.42.42.2
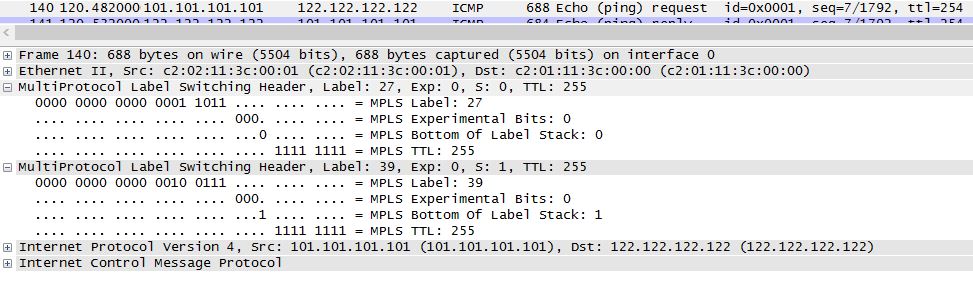
P1 swap the outer tag used for MPLS switching (27 to 26)
P1#sh mpls forwarding-table | i 7.7.7.7
27 26 7.7.7.7/32 70630 Fa2/0 23.23.23.3
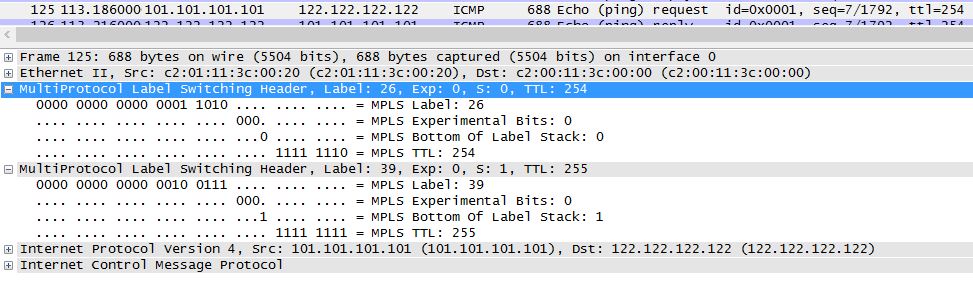
P2 remove the outer tag (Penutilmate Hop Popping, PHP). This operation is done one hop before the PE router. Only the VPN tag remains.
P2#sh mpls forwarding-table | i 7.7.7.7
26 Pop tag 7.7.7.7/32 199791 Fa2/0 37.37.37.7
The packet is then oriented to the right interface on the PE router:
PE4#sh ip bgp vpnv4 all labels
Network Next Hop In label/Out label
Route Distinguisher: 65000:1 (B)
101.101.101.101/32
4.4.4.4 nolabel/38
104.104.104.0/24 4.4.4.4 nolabel/39
122.122.122.122/32
124.124.124.12 39/nolabel
124.124.124.0/24 0.0.0.0 38/aggregate(B)
PE4#sh ip route vrf B eigrp
122.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 122.122.122.122
[90/156160] via 124.124.124.12, 02:21:57, FastEthernet0/1.12
Troubleshooting commands
PE1#sh ip vrf ?
WORD VPN Routing/Forwarding instance name
brief Brief VPN Routing/Forwarding instance information
detail Detailed VPN Routing/Forwarding instance information
id Show VPN Routing/Forwarding VPN-ID information
interfaces Show VPN Routing/Forwarding interface information
| Output modifiers
PE1#sh ip route vrf X
PE1#sh ip bgp vpnv4 ?
all Display information about all VPNv4 NLRIs
rd Display information for a route distinguisher
vrf Display information for a VPN Routing/Forwarding instance
PE1#sh ip bgp vpnv4 vrf B ?
A.B.C.D IP prefix /, e.g., 35.0.0.0/8
A.B.C.D Network in the BGP routing table to display
cidr-only Display only routes with non-natural netmasks
community Display routes matching the communities
community-list Display routes matching the community-list
dampening Display detailed information about dampening
extcommunity-list Display routes matching the extcommunity-list
filter-list Display routes conforming to the filter-list
inconsistent-as Display only routes with inconsistent origin ASs
labels Display BGP labels for prefixes
neighbors Detailed information on TCP and BGP neighbor connections
oer-paths Display all oer controlled paths
paths Path information
peer-group Display information on peer-groups
pending-prefixes Display prefixes pending deletion
prefix-list Display routes matching the prefix-list
quote-regexp Display routes matching the AS path "regular expression"
regexp Display routes matching the AS path regular expression
replication Display replication status of update-group(s)
rib-failure Display bgp routes that failed to install in the routing
table (RIB)
route-map Display routes matching the route-map
Route target extended community
PE1#sh ip bgp vpnv4 all 122.122.122.122/32
BGP routing table entry for 65000:1:122.122.122.122/32, version 22
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table B)
Flag: 0x820
Not advertised to any peer
Local
7.7.7.7 (metric 4) from 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1)
Origin incomplete, metric 156160, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
Extended Community: RT:65000:1 Cost:pre-bestpath:128:156160
0x8800:32768:0 0x8801:12:130560 0x8802:65281:25600 0x8803:65281:1500
Originator: 7.7.7.7, Cluster list: 1.1.1.1
mpls labels in/out nolabel/34
Download the configurations: MPLS-VPN-Lab.zip
RFCs 4364: http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4364