Fun with CARP : firewalls redundancy
CARP stands for Common Address Redundancy Protocol. It is a protocol developed by the OpenBSD team that aim to give a free, open source and reliable alternative to well-known HA protocols HSRP (Cisco) and VRRP (IETF).
This protocol could be used to achieve basic redundancy (failover) but also load balancing. The interest is to combine it with other daemon synchronization protocols, for example with packet filter (PF, the OBSD firewall) and its synchronization protocol pfsync (packet filter synchronization).
As a consequence, CARP is generally set up between servers, routers, or firewalls.
In the following article CARP will be set up as failover mechanism between two openBSD PF firewalls and will be combined with Pfsync.
CARP will handle the virtual interface and keep alive tracking features. On the other side Pfsync will take care of state tables synchronization, between the two PF instances. Thanks to this, if a firewall goes down, all the connections will be kept alive because the second firewall is aware of their states: no down time!
For those of you who are familiar with HSRP or VRRP, CARP will not be difficult to grasp.
It manages a virtual IP and MAC address for the redundancy group. If the master fails, the new master will be elected based on the advertising frequency. If the master comes back online, it becomes the default backup. Periodically the master sends advertisements using IP multicast on port 112.
The history of CARP has not been calm and quiet. Basically the openBSD team wanted to produce a free implementation of the IETF standard VRRP. However, Cisco has patent rights on HSRP and VRRP, thus forced the OpenBSD team to create a whole new protocol.
But problems did not stop there. Once released, IETF and IANA denied CARP for cloudy reason (there are frictions between the openBSD team and IETF). Despite the insistence of the openBSD team, CARP (and Pfsync) were not ratified and no port number were assigned to them. As a consequence the port number 112 (VRRP) was chosen not to interfere with anything else.
CARP Packet
CARP packet contains:
- Version: CARP version, actually version 4
- Type: type
- VirtualHost ID: virtual group number
- AdvSkew: timers modification value
- AuthLen: size of counter field + md field
- Demotion: counter that delayed the election (useful in some cases where topology calculation takes time, BGP for example)
- AdvBase: advertisement timers values
- Checksum: packet integrity control
- Counter: Two counters used for replay detection
- SHA-1 HMAC: packet protection (wikipedia)
Installation
The lab environment consists in two firewalls running openBSD 5.1.
- LAN : 10.1.1.0/24
- Pfsync : 10.2.2.0/24
- WAN : 1.1.1.0/24
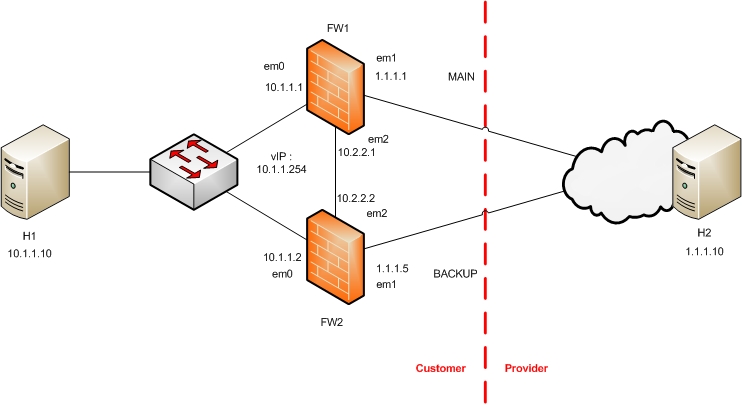
I set up a persistent configuration in this lab, so I will not use ifconfig or sysctl commands.
Master configuration
# cat /etc/hostname.em0 : LAN interface
inet 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
# cat /etc/hostname.em1 : WAN interface
inet 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
# vi /etc/hostname.carp0 : CARP interface for LAN vhid 1 - 10.1.1.254
inet 10.1.1.254 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.255 vhid 1 pass password advbase 1 advskew 0
The CARP interface is configured with the following values: virtual IP address, virtual host ID (vhid), redundancy group password, advbase and advskew. These last two values are used to calculate the time (in seconds) between each CARP advertisement. This interval is calculated as follows:
(advbase+ (advskew / 255) with 1 < advbase < 255 and 0 < advskew < 254
Advbase (advertisement base) is the base interval for CARP advertisement. Setting a higher advbase value (by default 1 second) will lower the network traffic, but will increase the delay when a new master election occur.
Advskew (advertisement skew) is a value that will modify the base interval for advertisement. A smaller value of advskew will result in a higher number of advertisement sent by the host. This will improve this host’s chances to become the master. On the other hand, a higher advskew value will increase the interval between the advertisements.
These two values are important because the CARP election process is based upon the frequency of advertisement. As a consequence the node that will send advertisement at a higher frequency (the one who speaks more) will be elected as master.
# vi /etc/sysctl.conf
net.inet.ip.forwarding=1 # IP forwarding
net.inet.carp.preempt=1 # CARP preemption
net.inet.carp.log=2 # activate CARP log
net.inet.carp.allow=1 # allow incoming CARP packet
CARP log levels: 0 to 7 corresponding to syslog facilities Default level: 2, only CARP state changes are logged.
Do not forget to reboot in order to fix the configuration.
# reboot
Backup configuration
# cat /etc/hostname.em0 : LAN interface
inet 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
# cat /etc/hostname.em1 : WAN interface
inet 2.2.2.1 255.255.255.0
# vi /etc/hostname.carp0 : CARP interface for LAN vhid 1 - 10.1.1.254
inet 10.1.1.254 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.255 vhid 1 pass password advbase 1 advskew 100
# vi /etc/sysctl.conf
net.inet.ip.forwarding=1 # IP forwarding
net.inet.carp.preempt=1 # CARP preemption
net.inet.carp.log=2 # activate CARP log
net.inet.carp.allow=1 # allow incoming CARP packet
# reboot
Verify the configuration
You can verify your configuration, initiating a failover with the following commands:
Master:
# ifconfig em0
em0: flags=8b43 mtu 1500
lladdr 08:00:27:cb:77:03
priority: 0
media: Ethernet autoselect (1000baseT full-duplex)
status: active
inet 10.1.1.1 netmask 0xffffff00 broadcast 10.1.1.255
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fecb:7703%em0 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x1
# ifconfig carp0
carp0: flags=8843 mtu 1500
lladdr 00:00:5e:00:01:01
priority: 0
carp: MASTER carpdev em0 vhid 1 advbase 1 advskew 0
groups: carp
status: master
inet6 fe80::200:5eff:fe00:101%carp0 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x6
inet 10.1.1.254 netmask 0xffffff00 broadcast 10.1.1.255
Backup:
# ifconfig em0
em0: flags=8b43 mtu 1500
lladdr 08:00:27:cb:77:03
priority: 0
media: Ethernet autoselect (1000baseT full-duplex)
status: active
inet 10.1.1.2 netmask 0xffffff00 broadcast 10.1.1.255
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fecb:7703%em0 prefixlen 64 duplicated scopeid 0x1
# ifconfig carp0
carp0: flags=8843 mtu 1500
lladdr 00:00:5e:00:01:01
priority: 0
carp: BACKUP carpdev em0 vhid 1 advbase 1 advskew 100
groups: carp
status: backup
inet6 fe80::200:5eff:fe00:101%carp0 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x6
inet 10.1.1.254 netmask 0xffffff00 broadcast 10.1.1.255
Master:
#ifconfig em0 down
Master:
# ifconfig carp0
carp0: flags=8803 mtu 1500
lladdr 00:00:5e:00:01:01
priority: 0
carp: INIT carpdev em0 vhid 1 advbase 1 advskew 0
groups: carp
status: invalid
inet6 fe80::200:5eff:fe00:101%carp0 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x6
inet 10.1.1.254 netmask 0xffffff00 broadcast 10.1.1.255
Backup:
# ifconfig carp0
carp0: flags=8843 mtu 1500
lladdr 00:00:5e:00:01:01
priority: 0
carp: MASTER carpdev em0 vhid 1 advbase 1 advskew 100
groups: carp
status: master
inet6 fe80::200:5eff:fe00:101%carp0 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x6
inet 10.1.1.254 netmask 0xffffff00 broadcast 10.1.1.255
Pfsync configuration
It is possible to implement pfsync in different ways:
- using the LAN interfaces of both gateways
- using a dedicated link
The first option is not recommended because your firewall state tables will flow through your network. It is less secured (some people run IPsec to create a secure channel, but my opinion is that we should keep things simple when it is possible to).
Though I will use a dedicated link between my two firewalls (cross-over cable).
Master:
# cat /etc/hostname.em2 : pfsync dedicated interface
inet 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.0
# vi /etc/hostname.pfsync0
syncdev em2
Backup:
# cat /etc/hostname.em2 : pfsync dedicated interface
inet 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
# vi /etc/hostname.pfsync0
syncdev em2
Up the interfaces on your nodes:
# ifconfig pfsync0 up
# ifconfig pfsync0
pfsync0: flags=41 mtu 1500
priority: 0
groups: carp pfsync
Packet Filter configuration
To let flow CARP and Pfsync in and out your firewalls, add the following rules:
# vi /etc/pf.conf
#CARP
pass on {em0} proto carp keep state
#Pfsync
set skip on em2
There is no need for filtering on PFsync interfaces so you can skip em2 interfaces: no processing time wasted.
Reload the rule-set:
# pfctl -Fa -f /etc/pf.conf
Verify the configuration
Check your rules:
# pfctl -s rules
pass all flags S/SA
pass on em0 proto carp all
block drop in on ! lo0 proto tcp from any to any port 6000:6010
Check your state table synchronization:
# pfctl -s state
BONUS : tracking script
Because we are in the case of a multihomed company network, we cannot run CARP on our WAN interfaces (different subnets, different ISPs)
In order to initiate a failover when one of the two internet links fails we need to create a script. This script will track the WAN interface state and do a software shutdown of the LAN interface when the internet link fails. As a consequence, the second node will take the master role.
# vi track-wan.ksh
#!/bin/ksh
i=1
# infinite loop
while [[ $i -eq 1 ]] ; do
# interface state variables
ifconfig em1 | grep UP
x=`echo $?`
ifconfig em0 | grep UP
y=`echo $?`
# if WAN is down, shutdown LAN
if [[ x -eq 1 ]]; then
ifconfig em0 down
# if WAN is up and LAN is down, then bring up LAN
elif [[ x -eq 0 && y -eq 1 ]]; then
ifconfig em0 up
# else wait 1 second
else
sleep 1
fi
done
# chmod +x track-wan.ksh
Startup script :
# vi /etc/rc.local
ksh track-wan.ksh &
Conclusion
CARP is actively maintained as part of the openBSD project. It is secured, it offers good performances, and achieve a great job with services synchronization protocols, however it is less employed than its counterparts. But because there is no professional support and a lack of skilled administrator, most of the companies hesitate to deploy such solution.
It is important to note that CARP is IPv6 compatible.
Links